A company tree is defined by a company and its entities (and each entity’s trade portfolios). This can be used for instance to represent a client account and its funds, or a bank’s business unit and its trading desks.
At company level, you can define company’s default valuation settings and preferred valuation data providers. These can also be overriden at entity level.
Once the company tree has been defined, you can create portfolio(s) which will hold the trades whose details can be used for PV calculation or valuation data anomaly detection.
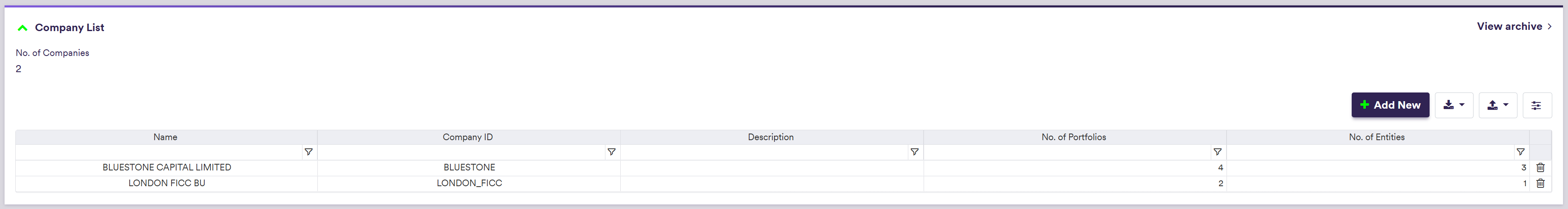
Xplain offers two pre-configured options - ‘BLUESTONE’ and ‘LONDON_FICC’ - which are available as off-the-shelf to use when performing your valuations or valuation data anomaly detection. For more details, please refer to our sandbox environment page.
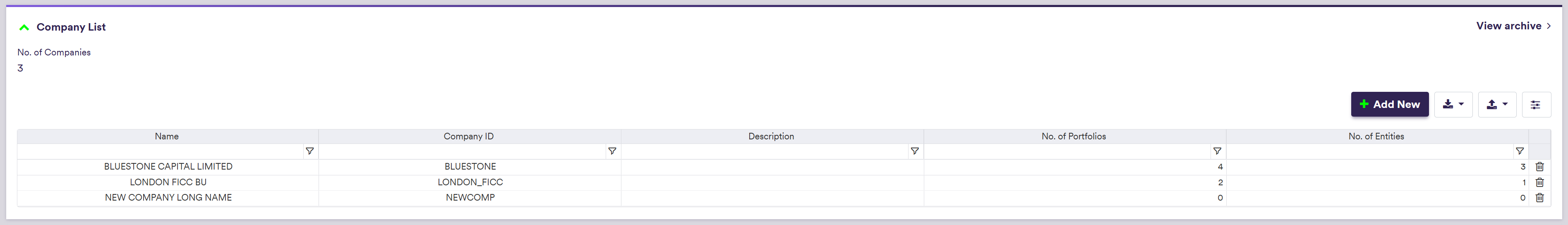
Company Tree Example
You can use the predefined ‘LONDON_FICC’ company (with its ‘RATES_DESK’ entity), or define your own independently. This page will guide you through the process using an example: defining a ‘NEWCOMP’ with a ‘NEWENT’ that replicates ‘LONDON_FICC/RATES_DESK/’. This will be used with the ‘NEWPORTFOLIO’ example. You can download the example *.CSV_ data import files here.
On this page, we will discuss how to:
- define a company tree
- define company’s default settings for valuation and valuation data provider (*)
(*) Defining valuation data providers is only relevant for the purpose of valuation data anomaly detection.
Company Tree Definition
The three steps required to define a company tree are as follows:
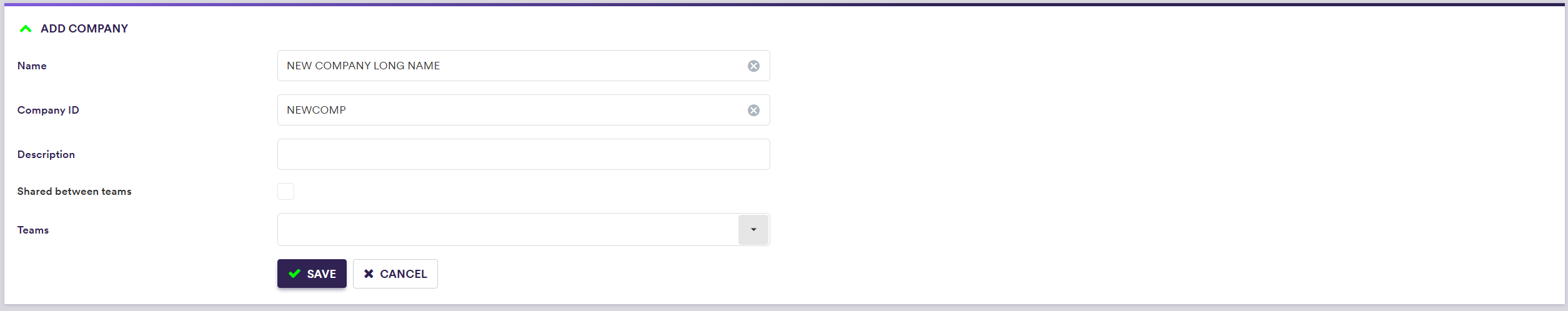
1. Creating a Company
Under
To manually create a company, click on
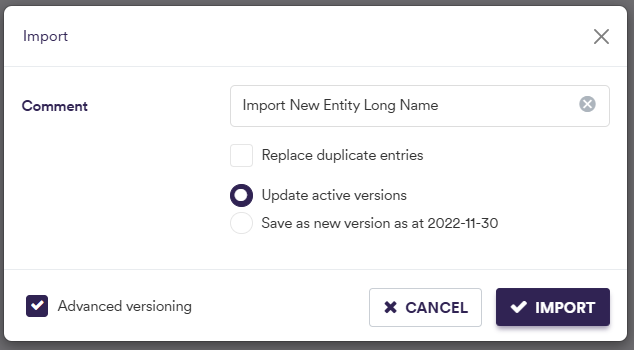
To import a company (or a list of companies), click on and select the relevant company list definition .CSV import file.
You can download the import file template here ![]() .
.
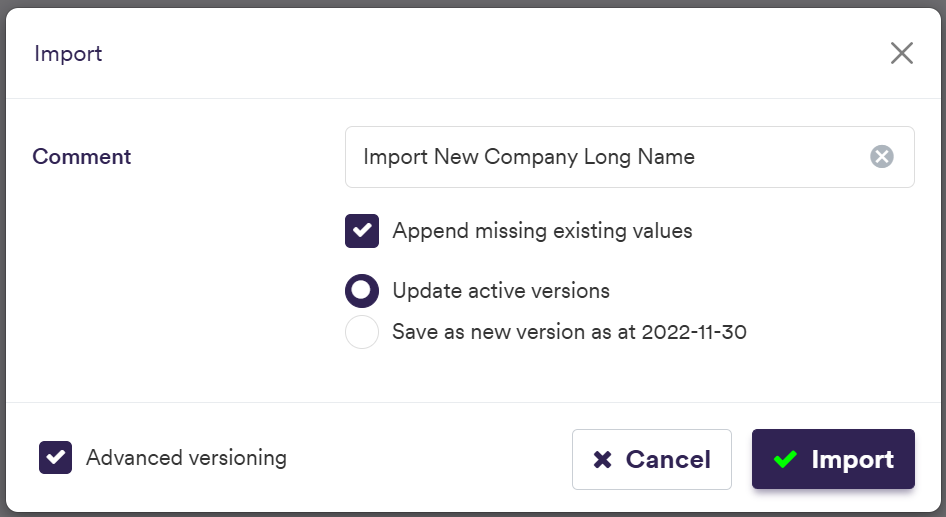
A description of the company’s attributes and corresponding permissible values are set out in the table below.
2. Adding an Entity
Under
Under
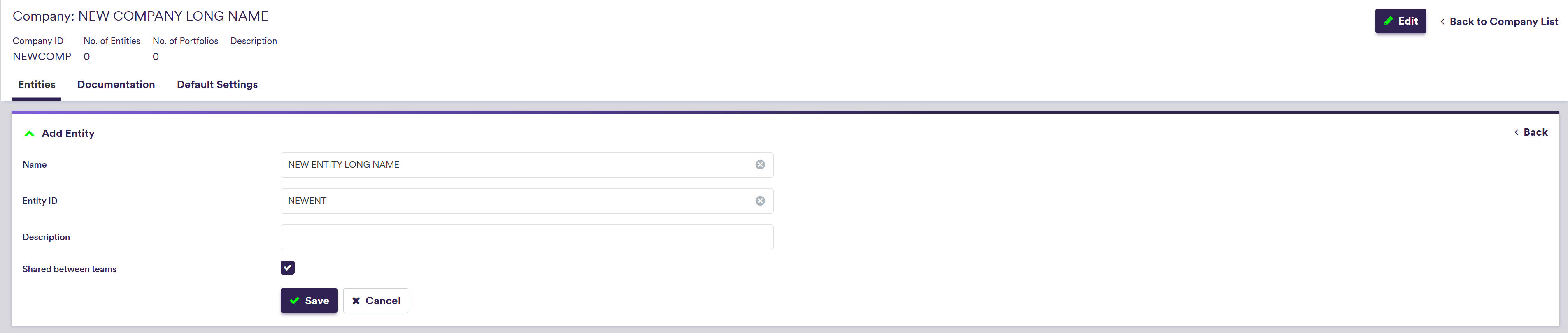
To import a company (or a list of companies), click on and select the relevant company list definition .CSV file.
You can download the import file template here ![]() .
.
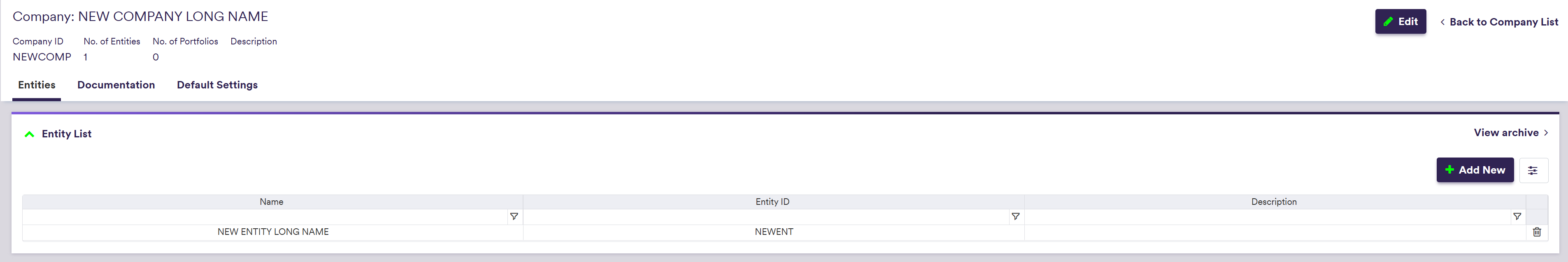
A description of an entity’s attributes and corresponding permissible values are set out in the table below.
3. Uploading Documentation
Under
Company's Default Settings
There are two types of default settings that can be defined at company level:
- company’s default valuation settings
- company’s default valuation data provider settings
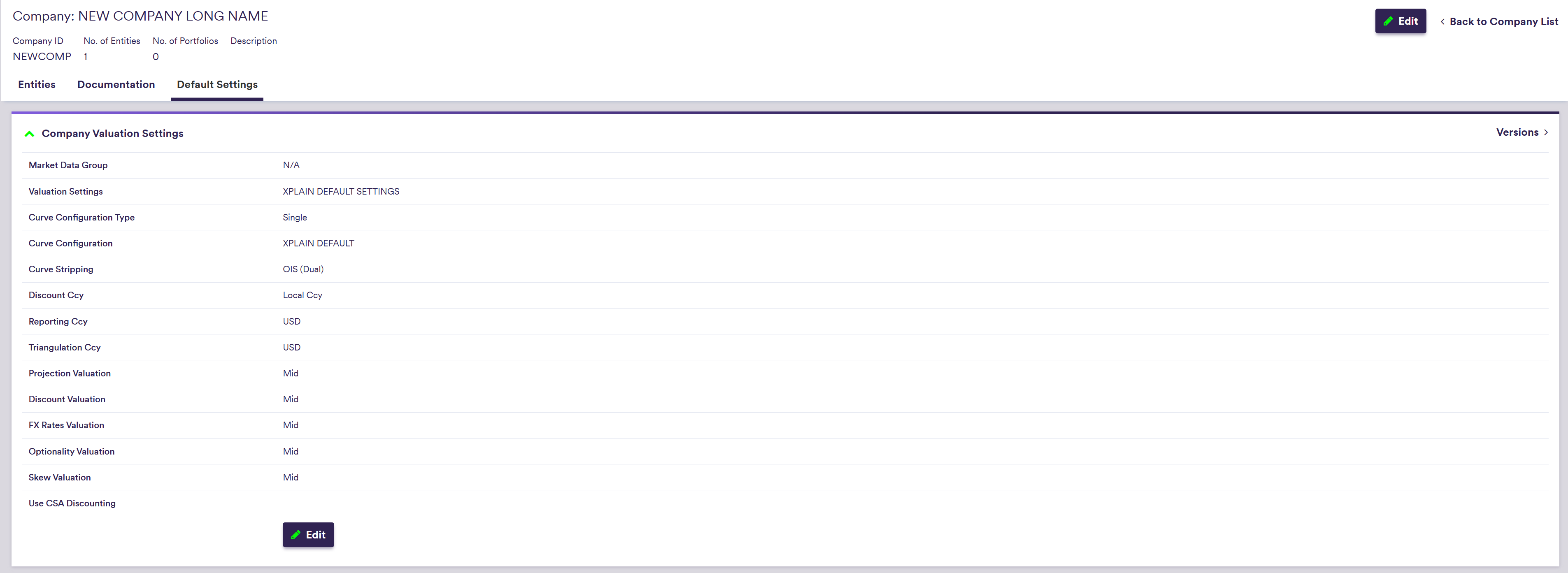
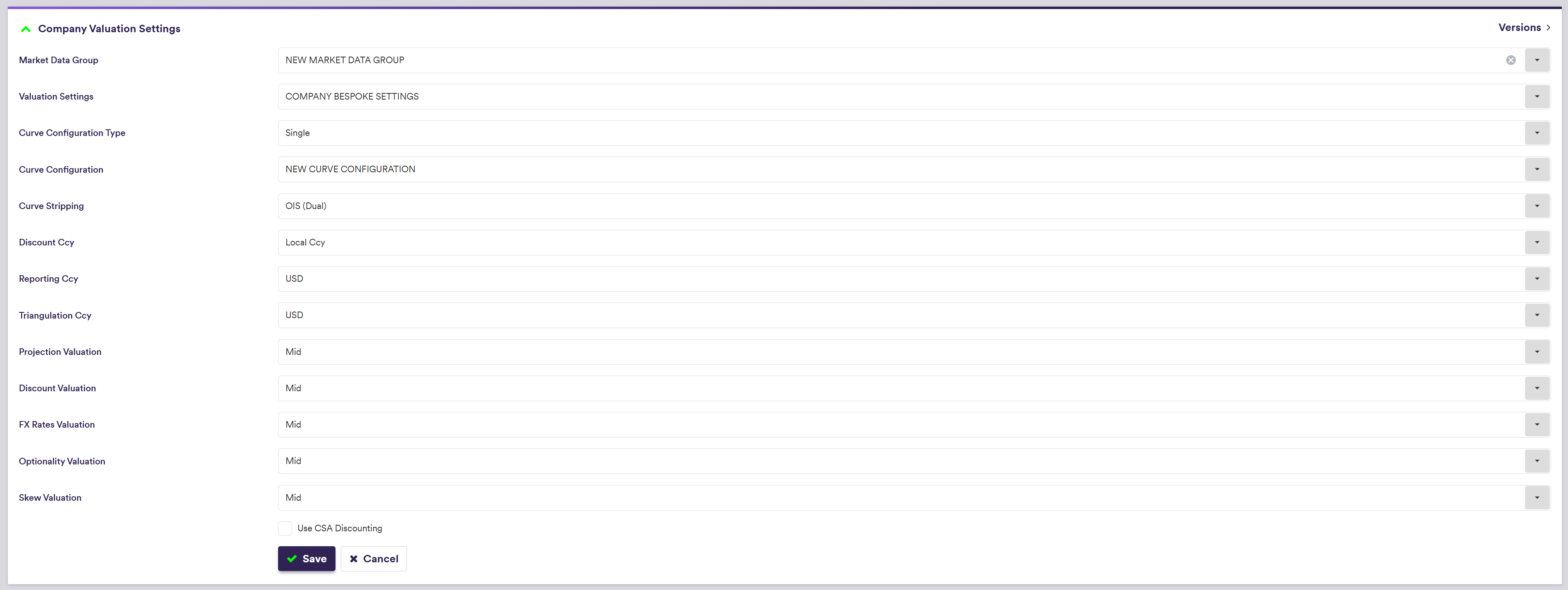
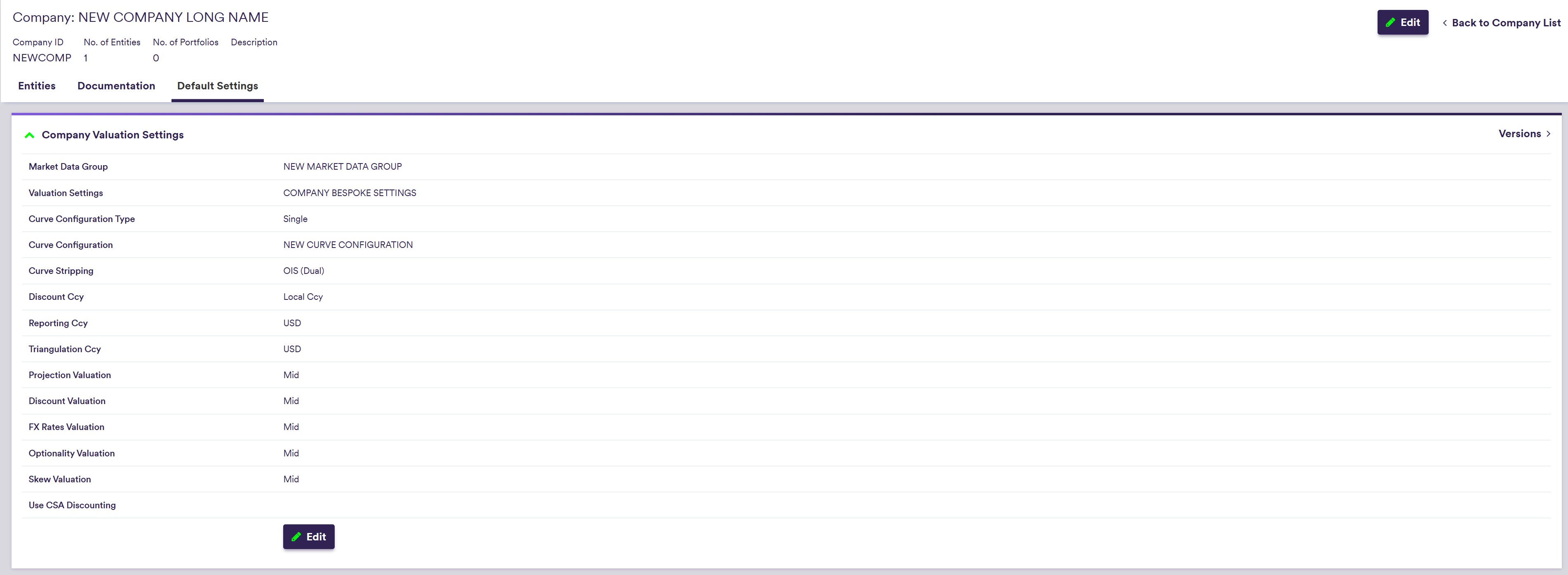
Default valuation settings includes preferred:
- curve configuration,
- market data group,
- discounting settings and
- market side valuation (bid, mid or offer).
They will automatically be applied when valuing trades prior to running a valuation data anomaly detection.
However, you can override them prior to running a manual PV calculation.
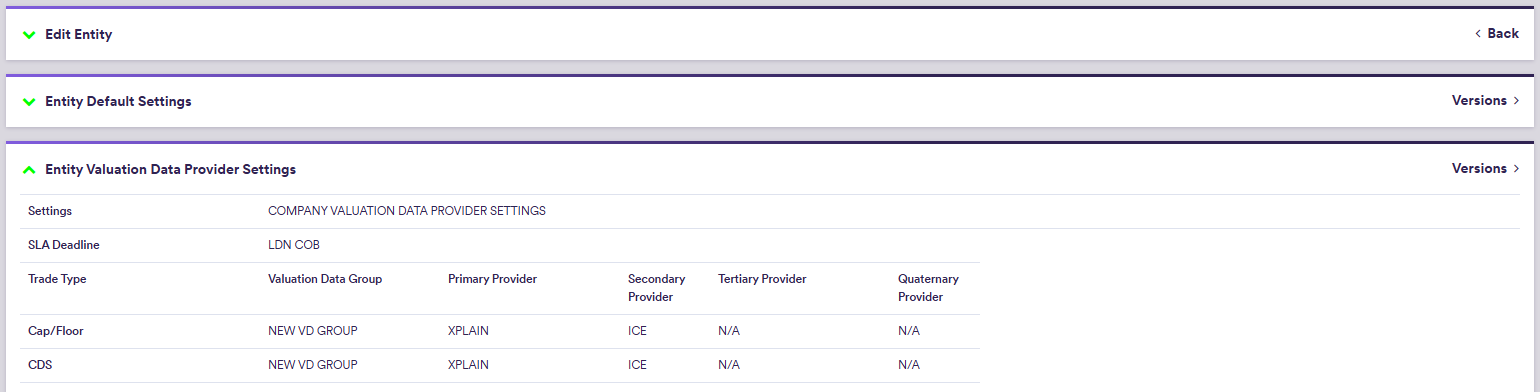
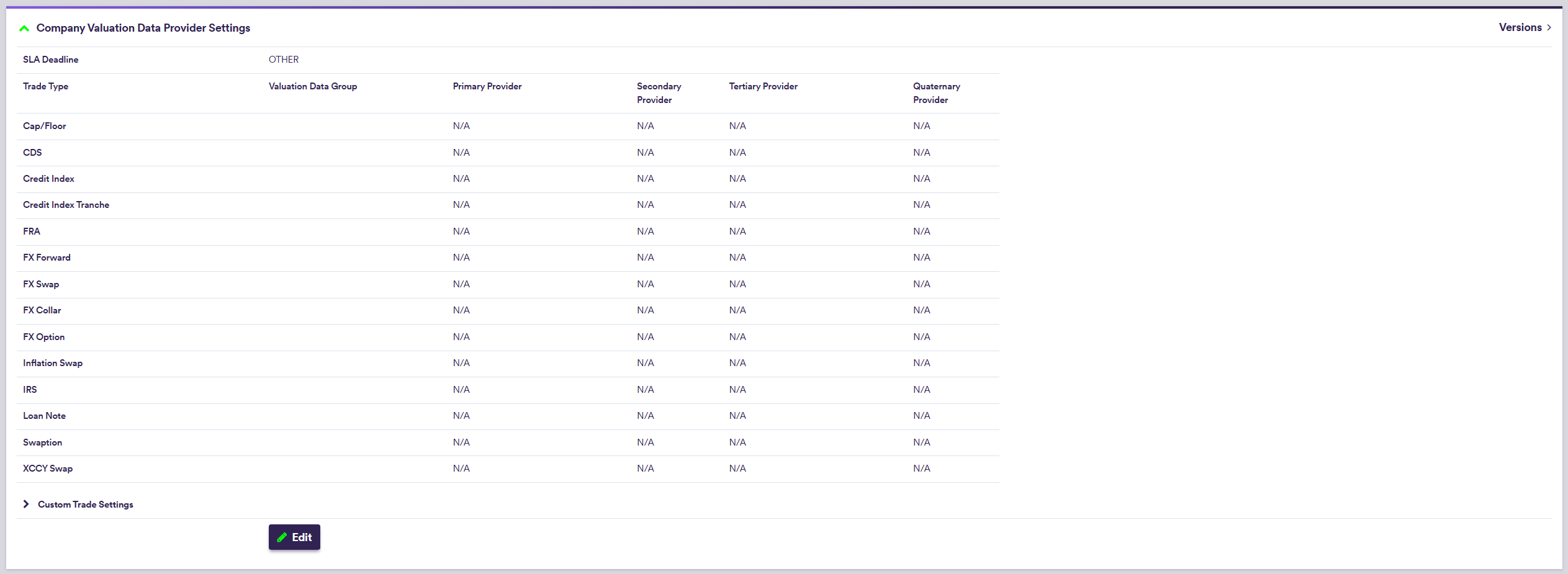
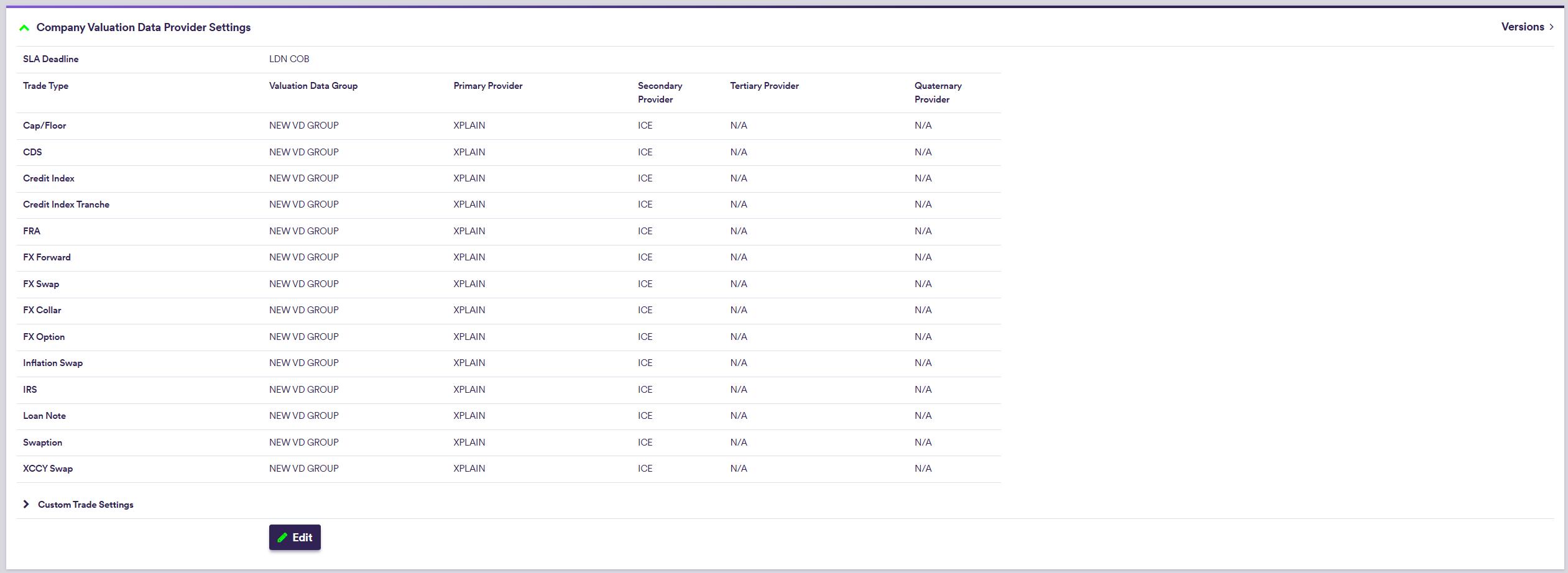
Default valuation data settings, which are only relevant for the purpose of valuation data anomaly detection, comprise SLA deadline time and, on a trade type basis, preferred valuation data group(s) and data providers (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary, as applicable).
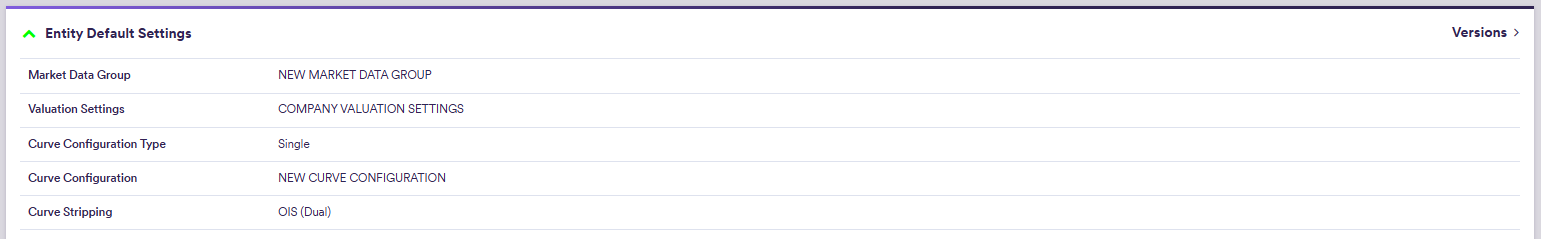
Entity settings are inherited from the parent company, but they can be overriden at entity level.
Part of our ‘NEWCOMP’ example that replicates ‘LONDON_FICC’, this section will guide you through the process of defining default settings at company and entity level.
1. Company’s Default Valuation Settings
Under
Xplain’s global valuation settings, which are defined under
2. Company’s Default Valuation Data Provider Settings
Under
The Default Provider can be used to populate primary to quaternary provider settings using the
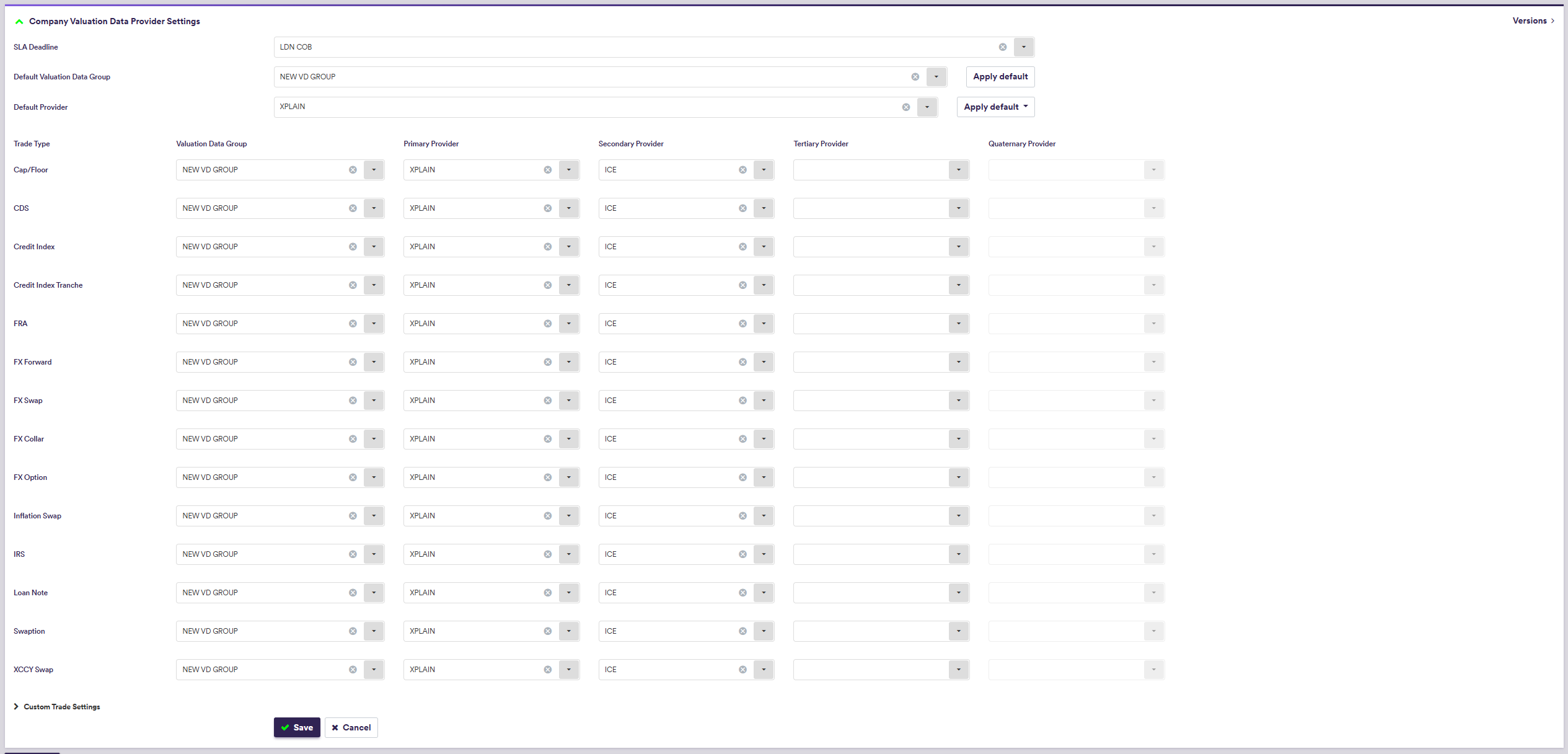
3. Entity's Default Settings
Entity’s settings are inherited by default from the parent company.
Under